A password manager is an excellent tool for organizing and protecting your online accounts, but only if you know how to use a password manager effectively. Many people underestimate the security that password managers offer. If you’re serious about keeping your data safe, here are six crucial password manager best practices you must implement immediately.
Key Takeaways
- The double-blind password strategy is critical for maximum security.
- Email aliases can significantly boost your online privacy.
- Two-factor authentication (2FA) is essential for securing your password manager.
- Randomized answers to security questions protect you from social engineering.
- Family-wide adoption of password managers ensures stronger overall security.
- An emergency access file safeguards account access in unexpected situations.
While we’re going to explain the fundamentals of password managers, if you want to jump into the 6 best practices for password managers, you can do that here:
- Use the Double-Blind Password Strategy
- Use Email Aliases for Privacy
- Enable 2-Factor Authentication (2FA)
- Create Random Answers for Security Questions
- Secure Your Family’s Digital Life
- Don’t Forget the Emergency Access File!
Note: Some of the links in this article may be affiliate links, which means that at no extra cost to you, I may be compensated if you choose to use one of the services listed. I only recommend what I personally have used, and I appreciate your support!
Password Management Essentials
Password managers are essential tools for securely storing and managing your login credentials, ensuring quick and safe access to your online accounts across all your devices. They offer convenient features like automatic password generation, auto-fill capabilities, and secure credential sharing. By leveraging a password manager, you significantly enhance your digital security and gain better control over your online presence.
When selecting a good password manager, consider:
- Ease of use and user-friendly interfaces.
- Cross-device compatibility (Windows, macOS, Linux, Android, iOS).
- Availability of self-hosted options for enhanced data control and privacy.
- Advanced security measures such as biometric authentication and hardware security keys.
- Independent security audits and certifications (e.g., SOC 2, ISO 27001).
Read reviews from trusted sources to compare different password managers and ensure you choose a reputable program that meets your specific needs.
Choosing the right password manager with these features ensures stronger protection for your personal data and a smoother, more secure online experience.
How Do Password Managers Work?
When you set up a password manager, you create a master password, which is the key to encrypting and decrypting all your stored passwords. These applications use robust encryption to protect your stored passwords, ensuring that only authorized users can access them.
Password managers secure your login information by encrypting credentials directly on your device before securely syncing them to the cloud. Core functionalities include:
- Encryption: Credentials encrypted locally, accessible only with your master password. By not storing your master password on the company’s servers, the risk of being hacked is significantly reduced, as attackers have no central repository to target.
- Auto-Fill: Automatically populates login fields. This not only saves you the hassle of remembering multiple passwords but also ensures that you use strong, unique passwords for each account, significantly reducing the risk of password reuse and data breaches.
- Security Auditing: Identifies weak or reused passwords, prompting regular updates to strengthen security.
Many password managers come equipped with additional features to enhance your password security. These include password generation tools that create complex passwords, password strength analysis to identify weak passwords, and alerts for potential security breaches. Some even offer multi-factor authentication, adding an extra layer of security to your login process.
By using a password manager, you can protect your online accounts more effectively, reduce the risk of data breaches, and ensure that your login credentials are always secure.
1. The Double-Blind Password Strategy
Storing all your passwords in one place seems risky to many people. To address this fear, implement the double blind password method (also known as salting or peppering). This approach ensures that neither you nor the password manager has the complete password, and it adds an extra layer of security by keeping the code transparent and inspectable. Here’s how it works:
- Generate a strong, random password using your password manager.
- Add an extra unique word, phrase, or numbers that only you know.
When logging in, your manager fills the saved password, and you manually type in your unique phrase. This keeps your real passwords completely hidden from both you and the password manager.
Example:
- Password manager generates: jR9#e2Q!
- You add: BeachVacation
- Actual password entered: jR9#e2Q!BeachVacation
This ensures that even if your password manager is breached, attackers still won’t have the full password, greatly enhancing your security.
2. Use Email Aliases for Better Privacy
Most users rely on a single email for all online services. Unfortunately, this can become a security weakness. Email aliases provide an additional protective layer, acting as a clever hack to enhance your online security:
- Security Enhancement: Hackers must know both your unique email alias and your password to access accounts.
- Privacy Management: If one alias is compromised or misused, you can quickly deactivate it without impacting your primary email.
Email aliases provide an additional protective layer, ensuring that even if one alias is compromised, unauthorized access to confidential information is prevented.
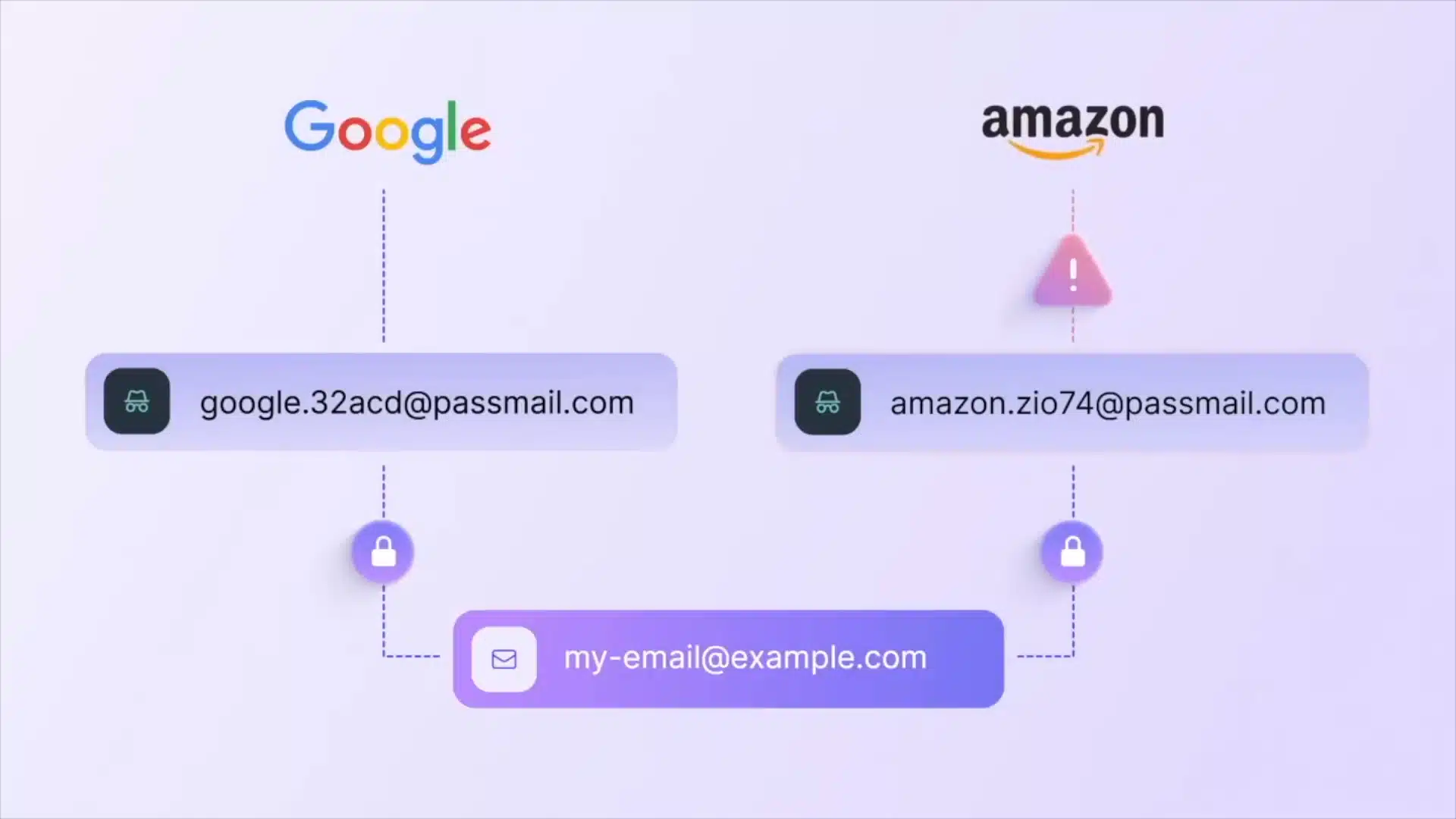
Platforms like ProtonMail or SimpleLogin enable creating multiple aliases easily. This practice ensures greater control over your digital identity and security.
3. Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
Two-factor authentication is a critical step in securing your password manager itself. Even the strongest password is vulnerable if it’s your only line of defense. When you enable multi factor authentication (MFA) and log into your password manager with 2FA enabled, you add an essential layer of protection.
By enabling 2FA, you introduce a second verification step, adding an essential layer of protection. Recommended 2FA methods include:
- Authenticator apps like Google Authenticator or Authy.
- Hardware security keys, such as YubiKey, provide physical verification.
Every time a new device attempts to access your password vault, you’ll need to verify it twice, significantly increasing your account’s security.
4. Create Random Answers for Security Questions
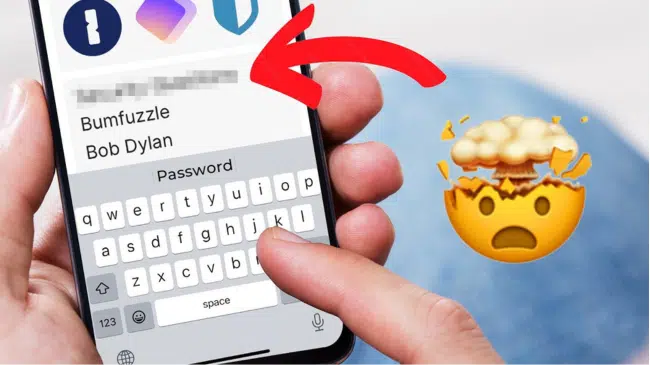
Many security questions ask for personal information easily discoverable online. To counter this vulnerability, create random answers and store them securely in your password manager. For example:
- Mother’s maiden name: Bumfuzzle
- Model of your first car: Bob Dylan
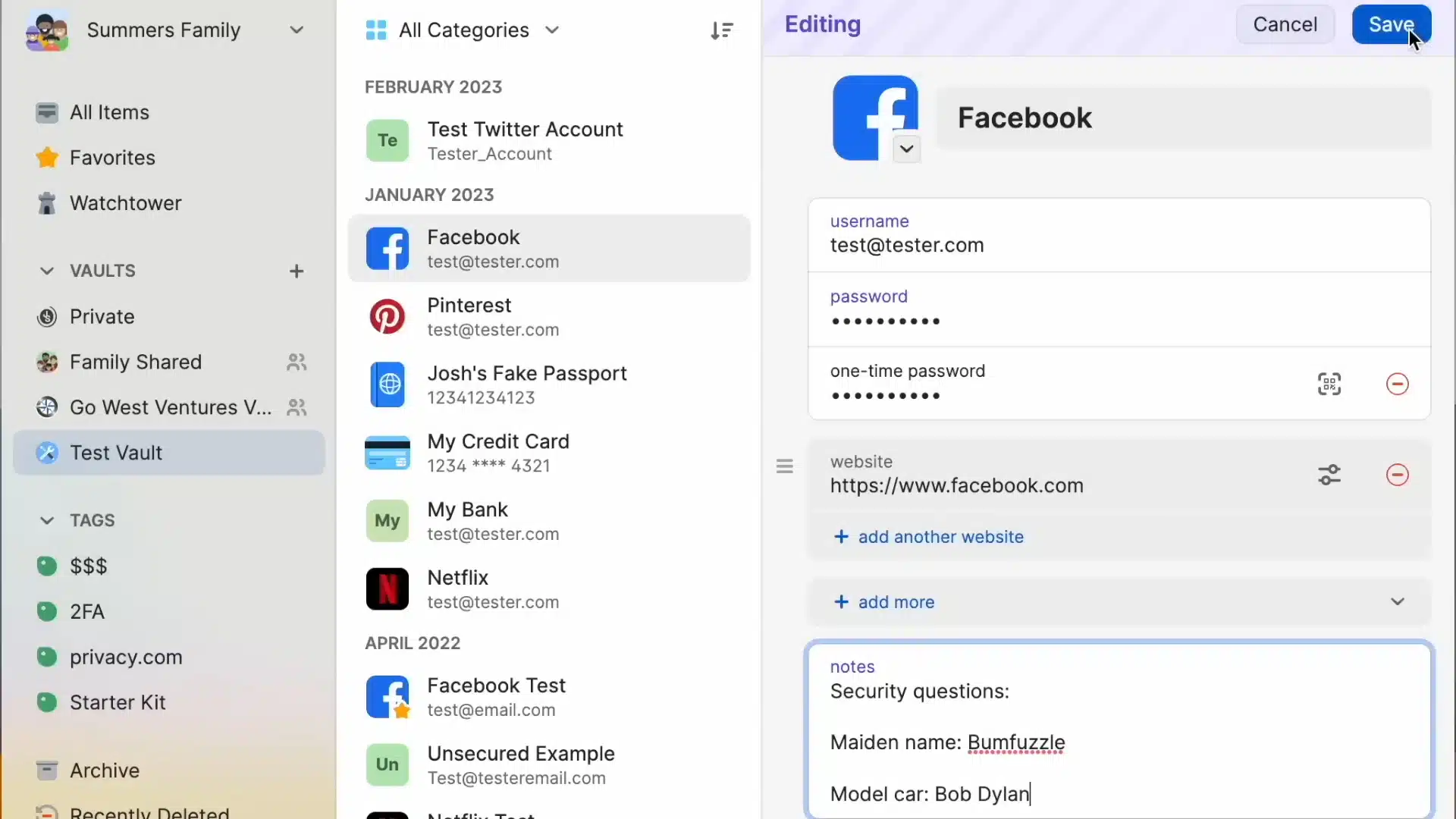
Using random answers makes it nearly impossible for cybercriminals to guess or research the correct answers, reducing your risk of falling victim to social engineering attacks. Store these random answers in the notes section of the password login so that you can easily find it when needed. Additionally, using a strong password in conjunction with these random answers further enhances your security.
5. Secure Your Family’s Digital Life Across All Your Devices
Your family’s security is as important as your own. Weak passwords or poor practices by family members can expose your accounts to risk. Here’s how you can encourage family-wide adoption of password managers:
- Install Password Managers on All Devices: Ensure family members have password managers on their computers, Android devices, and other mobile devices.
- Shared Vaults: Use shared vaults within the manager for common family accounts (streaming services, shopping sites).
- Educate and Demonstrate: Regularly discuss the importance of strong passwords and how password managers simplify secure practices.
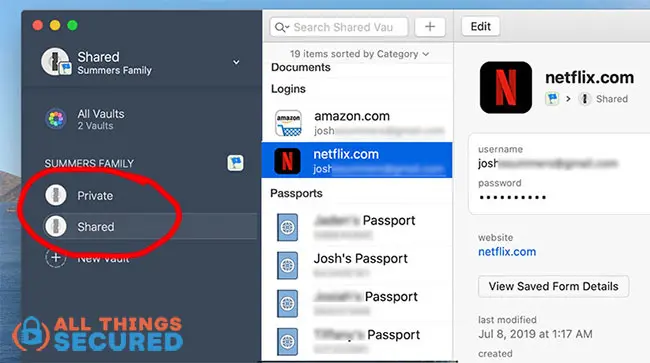
Making password security a collective family habit drastically reduces the likelihood of security breaches originating from your household. Organizations can also benefit from implementing robust password policies and security best practices to safeguard sensitive information and maintain compliance.
6. Emergency Access Files: Don’t Overlook This Critical Step
One of the most commonly overlooked password manager hacks is creating an emergency access file. This critical step ensures that your important accounts remain accessible and your data safe if you’re unable to access them yourself.
Here’s how to prepare an emergency access file effectively:
- Compile Essential Information: Document important accounts, login instructions, and steps to access your password manager.
- Secure Storage: Keep a physical or digital copy securely stored in a safe or with trusted family members.
- Regular Updates: Regularly review and update this document to maintain accuracy and relevance.
An emergency access file ensures your digital life remains secure and accessible, even in unforeseen circumstances. It is also crucial to ensure that the file meets all necessary security requirements to protect sensitive information.
Creating Complex Passwords
Creating complex passwords is a cornerstone of password security best practices. A complex password should include a mix of:
- Uppercase letters;
- Lowercase letters;
- Numbers;
- Special characters;
The length of the password is also crucial; longer passwords are generally more secure. Aim for a password that is at least 12 characters long, but remember that the longer, the better.
Using a passphrase—a sequence of words—can also be an effective way to create a complex password. For example, a memorable phrase like “SunsetBeach2023!” combines words, numbers, and special characters, making it both strong and easy to remember.
Password managers can assist in creating complex passwords by generating random combinations of characters. This ensures that your passwords are not only complex but also unique for each account, further reducing the risk of brute force attacks and dictionary attacks.
Avoid using easily guessable information, such as names or birthdays, in your passwords. By creating complex passwords, you significantly enhance your security and protect your online accounts from unauthorized access.
Master Password Protection
The master password is the key to unlocking your password manager’s vault, where all your stored passwords are kept. Therefore, it’s crucial to choose a strong and unique master password to protect your password manager. A good master password should be at least 12 characters long and include a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters.
Using a passphrase as a master password can be both secure and easier to remember. For instance, a phrase like “Fuzzy-Monkey-Secure-Vault-2025!” combines words, numbers, and special characters, making it robust and memorable.
Many password managers offer additional security features, such as two-factor authentication, to protect the master password. This adds an extra layer of security, ensuring that even if someone gains access to your master password, they would still need a second form of verification to access your vault.
It’s essential to keep your master password confidential and not share it with anyone. If your master password is ever compromised, change it immediately and update all your stored passwords. By protecting your master password, you ensure the security of all your stored passwords and, consequently, your online accounts.
Password Storage and Security
Password managers store passwords securely using advanced encryption techniques, protecting them from unauthorized access. When choosing a password manager, it’s essential to select a reputable one that follows best practices for password security.
Password managers store your passwords in a secure vault, which is protected by your master password. Some password managers also offer additional security features, such as zero-knowledge proof, ensuring that even the password manager itself cannot access your stored passwords.
Regularly updating and patching your password manager is crucial to maintaining its security. By keeping your software up-to-date, you protect yourself from potential vulnerabilities and ensure that your stored passwords remain secure.
Password managers can also help you identify and update weak passwords, further enhancing your password security. By following password security best practices and using a reputable password manager, you can protect your online accounts and safeguard your digital identity.
Disaster Recovery and Preparedness
Disaster recovery and preparedness are essential for ensuring the continuity of your password management in the event of a disaster. A good password manager should have a disaster recovery plan in place, which includes regular backups of your stored passwords.
It’s also crucial to have a plan for recovering your master password in case it is lost or compromised. Some password managers offer features like password inheritance, allowing you to designate a beneficiary who can access your stored passwords in the event of your death or incapacitation.
By having a disaster recovery plan, you can quickly recover your passwords and access your online accounts in the event of a disaster. Regularly review and update your disaster recovery plan to ensure its effectiveness.
Being prepared for disasters minimizes the risk of password-related disruptions and ensures the continuity of your online activities. Password managers can also help you identify and mitigate potential risks, such as brute force attacks and dictionary attacks, further enhancing your password security.
Choosing the Best Password Manager
Selecting the right password manager is crucial. Here are key factors to consider:
- Strong Encryption: Choose a manager with robust encryption protocols (AES-256 encryption). Additionally, consider solutions that allow data to be stored on the company’s servers, providing enhanced control over sensitive information and security.
- Ease of Use: Ensure the interface is user-friendly to encourage consistent usage.
- 2FA Support: Look for built-in two-factor authentication.
- Cross-Platform Functionality: A good manager will work seamlessly across multiple devices and browsers, including Windows, MacOS, and Linux.
- Web Security: Ensure the password manager offers features like browser extensions and web monitoring for potential data leaks and phishing attacks.
Popular trusted options include Proton Pass, 1Password, and Bitwarden, each offering unique features suited to different user needs. Integrating these solutions can facilitate smoother operations for IT and security teams, centralizing and automating password management tasks to mitigate risks and protect the organization.
Final Thoughts
Implementing these hacks transforms your password manager from a simple tool into a cornerstone of robust online security. By following these steps, you protect yourself and your family from potential cyber threats, ensuring peace of mind and secure digital experiences. Additionally, these practices play a crucial role in ensuring compliance with industry regulations and organizational policies.

